AKAVA Therapeutics’ programs are all based on some type of inhibition: inhibition of protein aggregation, inhibition of enzymes, and inhibition of tumor growth. We, therefore, refer to our therapeutics as inhibition therapeutics.
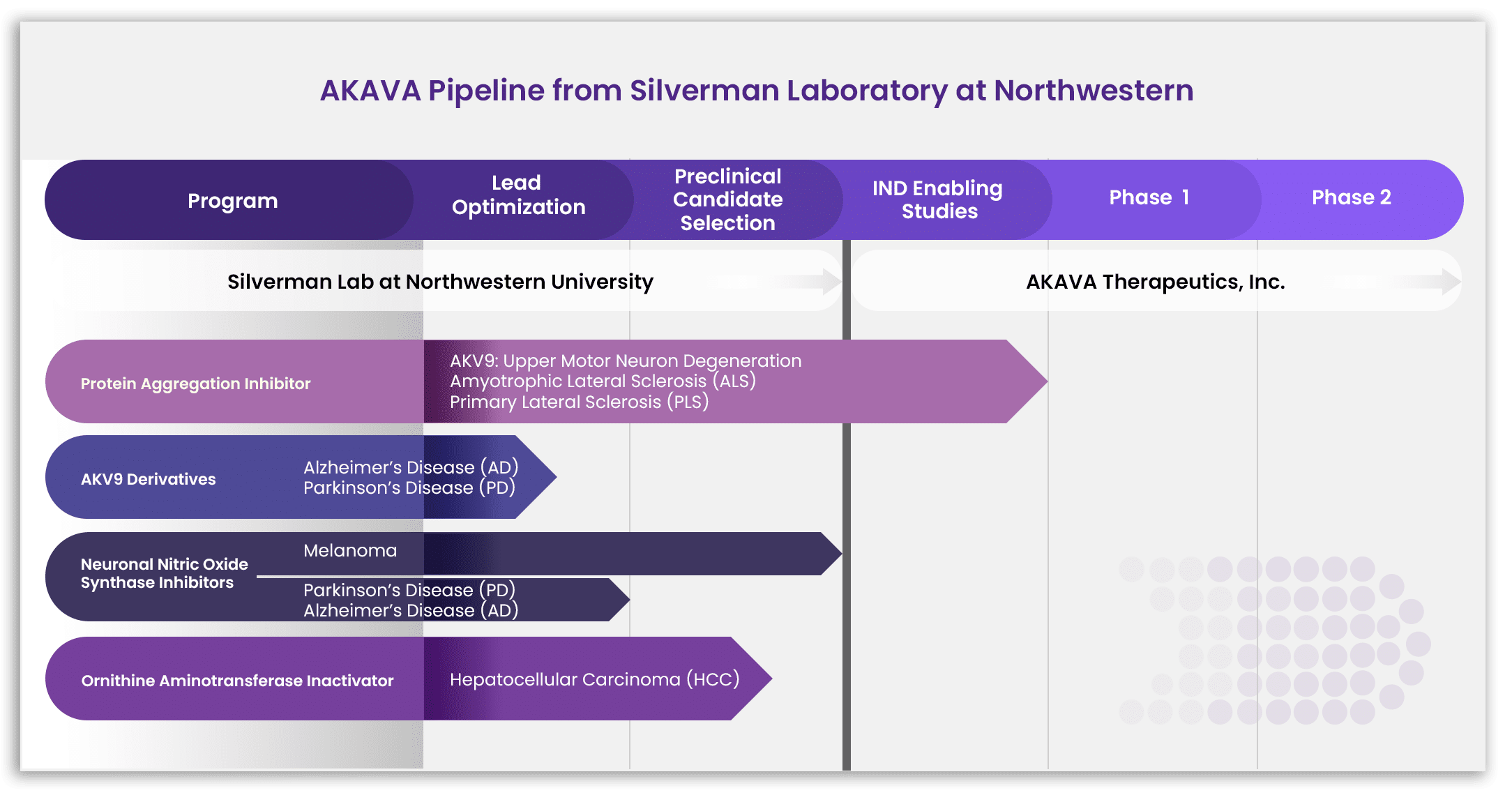
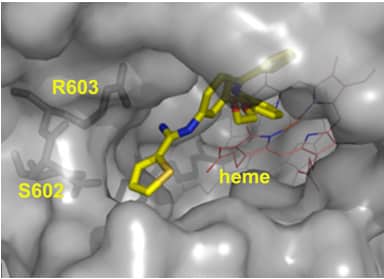
AKV9, Protein Aggregation Inhibitor
This compound is currently in IND-enabling studies, with GLP animal toxicology under contract. Watch the Video
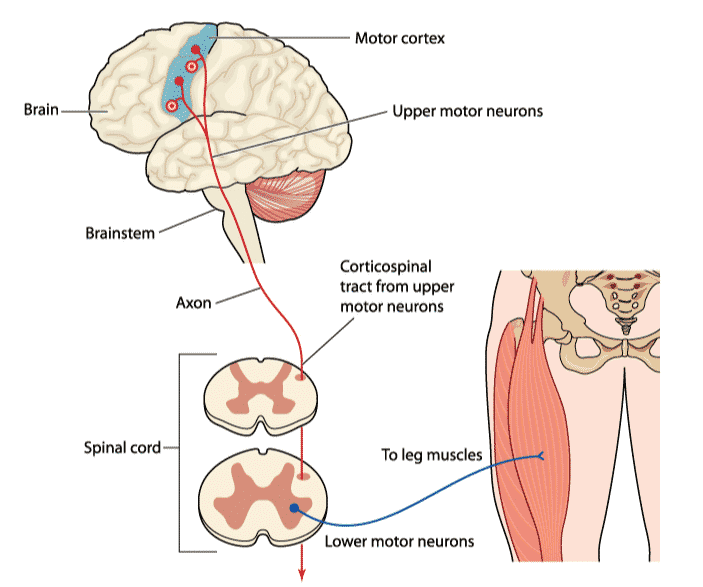
Protein aggregation is a hallmark of all neurodegenerative diseases, including ALS and other upper motor neuron (UMN) diseases.
AKV9 is the first compound reported to improve the health of diseased upper motor neurons.
- UMNs degenerate early in ALS; inhibition of protein aggregation caused by various gene mutations maintains the health of UMNs.
- Dose-dependent treatment with AKV9 of mice having two different ALS gene mutations led to overall improvement of UMN health, becoming comparable to healthy control mice, after 60 days of treatment.
- Upon AKV9 treatment, diseased UMNs retained integrity of their mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and stability of their apical dendrites.
- Axon length, branching, and arborization increase with AKV9 treatment in vitro; remarkably, a combination of AKV9 with the FDA-approved ALS drugs riluzole and edaravone enhances this effect.
- Mouse grip strength and body weight are retained.
- Currently, there is no translation from extension of lifespan in animal models to extension of lifespan in humans, but UMNs in mouse models of ALS and UMNs in ALS patients share the same pathology at a cellular level which should lead to translation in humans and ultimately, effective treatments for patients.
Click for more information about ALS and other UMN diseases:
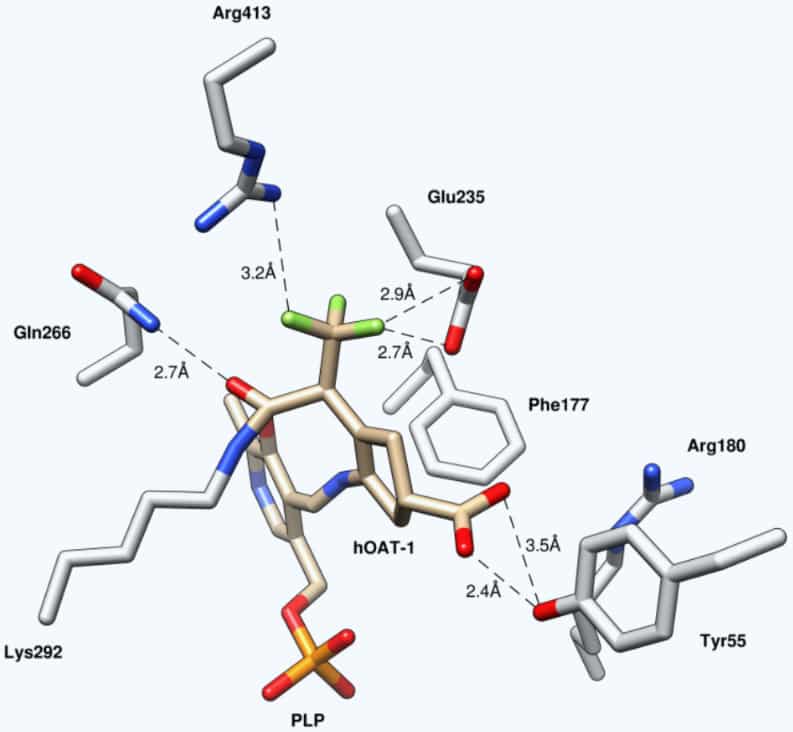
Ornithine Aminotransferase Inactivators
We currently have five molecules that are potent and selective ornithine aminotransferase inactivators with which we are carrying out comparative efficacy and toxicology studies to decide which one to bring into IND-enabling studies.
- The gene encoding for ornithine aminotransferase (OAT) is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
- Inactivation of OAT inhibits secretion of alpha-fetoprotein, a biomarker for HCC, in mice implanted with human HCC
- Inactivation of OAT inhibits growth of HCC in mice implanted with human HCC
Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitors
One nNOS inhibitor has been synthesized in a large quantity, and further animal studies are underway in cerebral palsy. Two other nNOS inhibitors are in preclinical studies for melanoma.
- Neurodegenerative diseases include any disease in which neurons lose function, degrade, and eventually die.
- Melanoma is a skin cancer that is caused by uncontrollable growth of the skin cells that produce melanin (melanocytes).
- Neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) is an enzyme that catalyzes production of nitric oxide, a free radical that can degrade neurons in the brain or melanocytes in the skin (melanocytes derive from a neural crest).
- Inhibition of nNOS is an approach to treat neurodegeneration or melanoma